The CardioNet Project is an interdisciplinary applicative research project that is consistent with the community program of public health launched by the Romanian Health Ministry and which follows the actual general trends in cardiology and geriatrics, at the European and world level.
The CardioNet Project aims at realizing a pilot system of telecardiology for remote and continuous registering and monitoring of the state of the patients with heart problems, integrated into an intelligent network based on all the partner units. The system will ensure interoperability and information exchange between the main actors of the health system: autonomous medical applications, patients, family physicians, polyclinics, hospitals, and the Health Insurance House.
Based on the performed studies, the conclusion was that the CardioNET system should have an open, distributed and modular architecture, in order to allow its development and continuous update, by the addition of new components. The proposed system model will ensure the continuous monitoring of the patients with ischemic cardiopathy, of those with heart rhythm troubles and of those under anticoagulant treatment. In order to meet these requirements, sensors and fixed and / or mobile medical equipment will be used, which will be connected in a mixed communication network, cable-based and wireless.
The system will ensure the real-time exchange of medical information between the family physician, the polyclinic and the hospital. The system that will be created will ensure the exact knowledge of the medical antecedents and of the undertaken treatments as well as the evolution of certain pathologies.
The large-scale utilization of this system will contribute to the amelioration of the population's health state by improving the efficiency of the public health system and of the primary, secondary and tertiary health assistance, and also by a better addressability and compliance to the treatment by the patients.
The results of this project will be useful both to the cardiologist (by better patients statistics after the beginning of the specialized treatment), to the primary and secondary medical assistance (by interrogating the data bases and exchanging information between specialists) and to the patient (by increasing his / her compliance to the treatment, diminishing the discomfort determined by the visits to the family physician and to the cardiology specialist, reducing the time passed in the hospital, reducing the number of days of working incapacity)
In the figure below we present a general scheme of the computing medical system proposed in the framework of the CardioNET project. We have highlighted the system's actors and their interaction with the computing system.
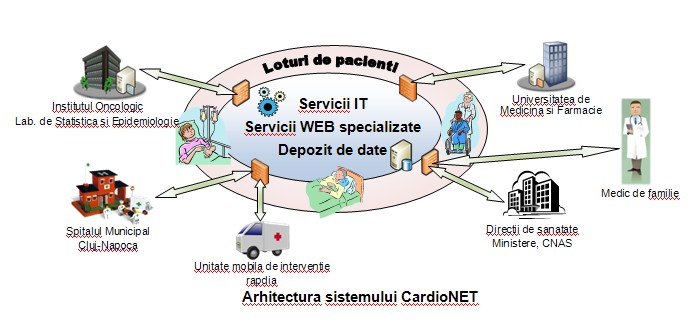
The modern ITC technologies used (SOAP, XML, web services, ontologies) will ensure the creation of state-of-the art electronic records with the patients' personal data and will ensure a high level of interoperability between heterogeneous systems.
The specific data structures will allow collecting, store and retrieving classical medical data, electrocardiographic data, including rhythm and leading troubles, as well as laboratory data concerning anticoagulant treatment.